The Extended Shelf Life (ESL) milk market, globally as well in North America, is on a notable upswing, though not without challenges. This article explores ESL milk's advantages and factors influencing its shelf life, with a focus on the crucial roles of Filling Systems and Packaging in shelf-life management.
Emphasis is placed on the advantages of net weight filling systems, packaging decontamination options, and their role in safeguarding ESL milk. A video case study in the end depicting a milk manufacturer who entered the ESL market with the Serac Rinser-Filler-Capper brings these insights to life.
Milk Sensitivity and Its Shelf Life
Dairy products, such as milk, are highly sensitive to factors affecting quality, safety, and shelf life. Milk, characterized by being low acid with high water activity and low sugar content, is particularly susceptible to spores development, leading to a short shelf life in its raw form.
-Serac-DairyFoods.com.png)
To address sensitivity and ensure product safety, various processing techniques are employed with heat treatment, although micro-filtration is also possible nowadays. Common methods to eliminate spores in the bottling of milk include:
- Pasteurization (162°F for 15 seconds) for 7-15 days of shelf life.
- ESL (275°F for less than a second) for 30-45 days.
- ESL+ (280°F for 2 seconds) for 60-120 days.
- UHT (293°F for 4 seconds) for 90-360 days, Sterile.
What Sets ESL Milk Apart?
ESL, signifying an extended shelf life compared to conventional pasteurized milk, offers distinct advantages, including the potential to broaden sales channels and reduce food waste arising from unsellable items.
Consumer trends are also considered. The expectation for dairy products to be on refrigerated shelves in retail persists. Additionally, there's an emerging indication of preference for original and fresh products, perceived as healthier and more natural. The surge in clean labelling requires higher hygiene levels in milk bottling, adding further appeal to ESL processing.
However, it's essential to note that, like pasteurized milk, ESL & ESL-UHT products require a cold chain, differing from UHT products that can remain shelf-stable at room temperature. Regulatory considerations, especially those set by the US FDA for distributing products outside the cold chain, play a serious role in decision-making (source: FDA). ESL emerges as a pragmatic choice for companies navigating these complexities, offering a middle ground between traditional methods and aseptic alternatives.
Moreover, the decision to go ESL is influenced by ingredient tolerance to high temperatures, considering that sterilization, though effective, may alter the product's nature, impacting proteins, vitamins, taste, and color. ESL is considered non-sterile.
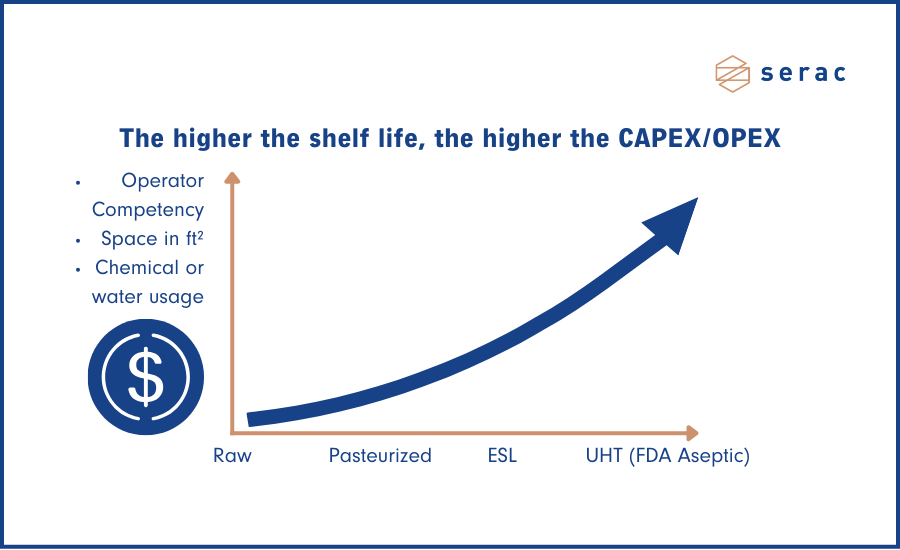
Financial considerations always play a crucial role in the decision-making process. The investment required varies significantly based on the chosen technology. While traditional methods like raw or pasteurized milk packing come with lower costs and operational simplicity, aseptic alternatives demand substantial investments, potentially reaching millions of dollars. ESL strategically positions itself as a balanced choice in this intricate decision-making process.
Bottling of ESL Milk: An Important Step to Protect the Shelf Life
For non-sterilized products like ESL milk, maintaining a cold chain is crucial to limit bacterial growth. The shelf life of dairy products in the cold chain is as good as the weakest link in the production chain.
The following factors all contribute to the overall shelf life:
- Raw milk quality
- Milk processing technology
- Filling technologies & environment
- Packaging containers
- Distribution temperature
- Storage temperature at customers
Milk is sensitive to light, particularly in the blue light spectrum, which degrades vitamins and proteins. While oxygen sensitivity is generally low in milk, certain additives like vegetable fat in infant milk formula may increase susceptibility.
This is why the choice of packaging in bottling ESL milk is a big factor. Different materials, such as polypropylene (PP), high-density polyethylene (HDP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and glass, offer varying levels of protection against factors like oxygen and light. Light barrier solutions, including titanium dioxide (TiO2), can be used to protect products from light degradation.
When it comes to filling equipment for milk bottling, securing a clean and easily maintainable product circuit is paramount. The product circuit directly impacts shelf life, and any compromise in hygiene can lead to a loss of product quality. Milk manufacturers must consider the sterility level of the product circuit, as well as decontamination of the bottles and caps.
However, apart from hygiene, conflicting requirements may arise when balancing an extended shelf life with emerging trends and financial consideration. For example, the longer the shelf life, the more protective the packaging material must be, yet it becomes less recyclable.
Therefore, milk product manufacturers must remain flexible and adaptive to the dynamic market landscape. There is no one-size-fits-all solution for milk products. To navigate the complexity of these decisions, businesses need a partner with extensive experience offering tailored solutions. The key lies in agility.
Serac Net Weight Filling Technology for ESL Milk
Net weight technology involves placing bottles on a scale, tearing the weight of the bottle, filling it to a predetermined level or weight, and verifying the accuracy of the filled product. This self-adjusting system allows for real-time adjustments to filling parameters, ensuring precise and consistent weights. If a bottle fails to meet the correct weight, it can be automatically rejected.
Here are how ESL milk manufacturers can benefit from this technology:
1.Hygienic Filling Solutions
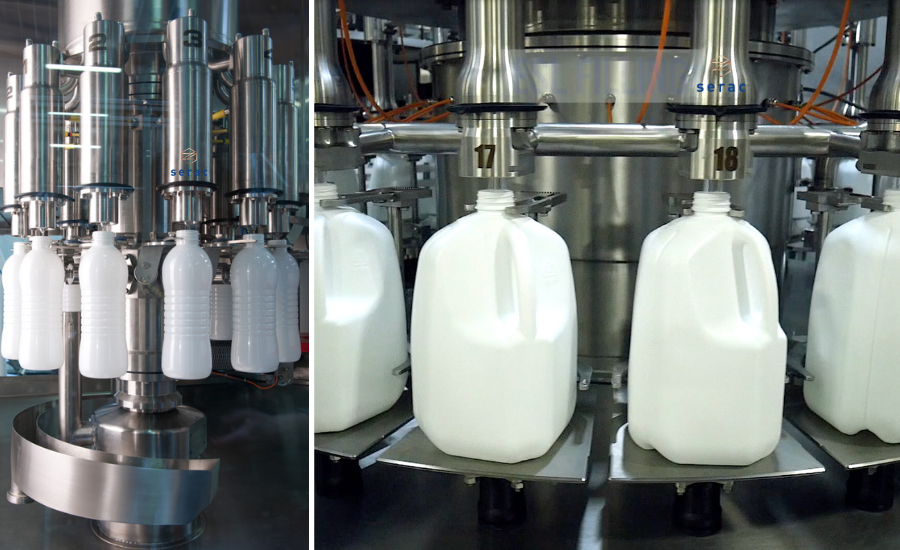

The use of a scale located outside the product circuit simplifies the system. The product circuit comprises a valve that opens and closes, making it easy to clean and reducing the risk of contamination.
Serac favors metal-to-metal construction, resulting in a product circuit with minimal maintenance requirements. This approach reduces the risk of contamination during maintenance and ensures long-term reliability.
Serac implements standard closed-loop CIP processes, using hot water at temperatures of 95 or 125 degrees Celsius for efficient cleaning. We offer CIP systems for Aseptic and Clean-In-Place processes, automating external surface cleaning to ensure optimal hygiene.
Airflow management, an often overlooked aspect in dairy filling. Serac employs HEPA filters in ultra-clean environments, creating a laminar flow of air that prevents contaminants from bouncing back onto the filling table. This meticulous approach reduces the risk of airborne mold and yeast contaminations.
Serac guarantees sterility by supplying its own cleaning and sterilization processes, ensuring the highest standards in ultra-clean filling.
2. Agile (Flexible & Versatile)
Net weight technology offers a high degree of flexibility and versatility in dairy filling. This system allows for the use of various materials like PET, metal, HDP, or glass on the same filler.
Additionally, it accommodates a wide range of container sizes, from 50ml to two liters, and can handle varying viscosities, from 1 to 40,000 cPo, and those with particles or fibers.
Quick changeovers ensure efficient transitions between different bottle formats.
3. Bottle & Cap Decontamination Options
Serac can propose a wide range of decontamination treatments on the containers, caps, and aluminium foil seals. Customers are given options that best suit their packaging decontamination needs: dry, liquid, or gas treatments.
For example, we can use H2O2 gas treatment to decontaminate most container formats. However, to be able to thoroughly sanitize containers with difficult parts to reach such as jugs with handles, we will recommend Peracetic Acid (PAA) liquid treatment.
-Serac-DairyFoods.com.png)
As Serac prioritizes innovations and sustainability, more environmentally friendly chemical-free decontamination treatments are also available, such as Pulsed Light and UV. Our latest decontamination technology in this category is BluStream®; a dry, physical sterilization treatment that uses electron beams to destroy microorganisms (at room temperature).
Showcase of Serac Rinser-Filler-Capper for ESL Milk
Here’s a video of Serac filling and capping machine with PAA decontamination treatment on jugs with handles and pulsed light on caps with foil for an ESL milk manufacturer in North America.
Serac Rinser Filler Capper for ESL milk and dairy products.
For more information about Serac Bottling Solutions for Milk and Other Liquid Dairy Products, visit: https://www.serac-group.com/serac-worldwide/filling-machines-for-milk-and-liquid-dairy-usa/



